Read Committed vs. Repeatable Read
- MySQL의 Isolation level은 전통적으로 Repeatable Read 를 default로 한다.
- 하지만 반드시 repeatable read가 필요한 경우에만 lock을 사용하고 그외에서는 committed 를 봐도 무방하다면, 다른 RDBMS와 같이 Read committed를 default Isolation level로 하는 건 어떨까.
- 막연하게 Read Committed가 lock contention이 더 줄고, 동시성에 더 좋을 것 같다.
- 그리고 Repeatable read 에서 long running query (혹은 슬프게도 transaction이 제대로 close되지 않아서)가 돌때 undo가 너무 많이 쌓여서 전체적으로 성능에 영향을 주는 상황도 회피할 수 있다.
Sysbench test and Isolation level
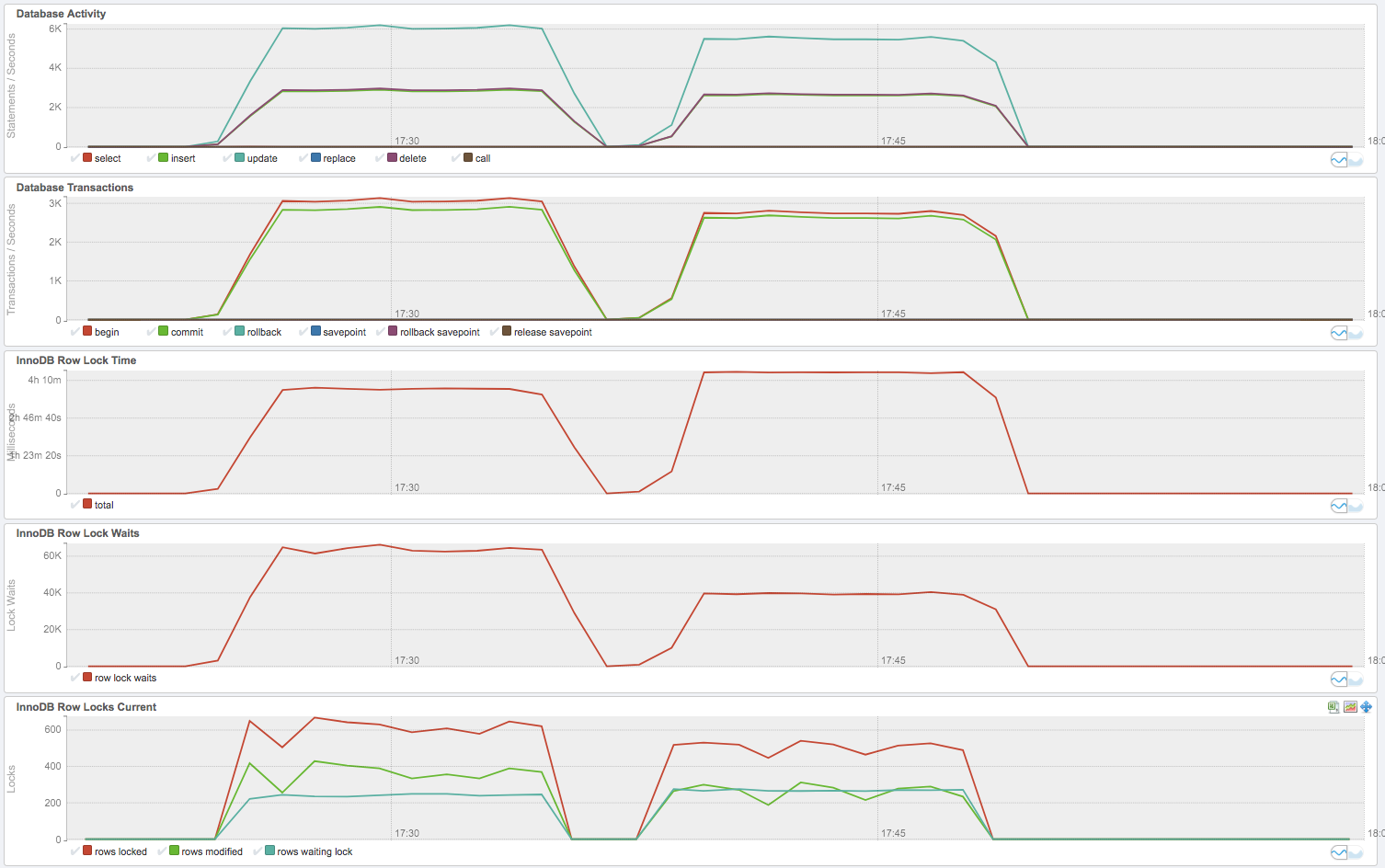
- 첫번째 결과그래프가 뭔가 throughput이 더 좋다.
- Lock wait은 두번째가 더 적다.
Isolation level만 변경한 것이다. 무엇이 Read Committed이고, 무엇이 Repeatable Read일까?
- 첫번째가 Repeatable read이고, 두번째가 Read Committed의 결과이다.
Basically,
트랜잭션 특성에 따라 결과는 다를 것이다. 이 테스트의 sysbench transaction은 간단한 update, delete, insert 하나씩 수행하게 되어있었다.
begin;
update ..;
update ..;
delete ..;
insert ..;
commit;
What makes a difference in throughput?
- 정답은 ReadView 이다.
- Reference: http://dimitrik.free.fr/blog/archives/2015/02/mysql-performance-impact-of-innodb-transaction-isolation-modes-in-mysql-57.html
- MySQL InnoDB의 transaction isolation / MVCC 은 ReadViews를 기반으로 동작한다.
- repeatable read는 transaction 시작할때 한번 readview 를 만든다.
- read-committed는 매 문장마다, 여기서는 4번, readview를 생성한다.
- Readview를 생성할때 mutex경합으로 인해 read-committed의 throughput이 줄어드는 것이다.
Conclusion
- 어디까지나 Max throughput의 문제이다.
- 일반적으로 3k TPS까지 쓸것인가. repeatable read로 인한 문제점이 더 자주 노출될 수도 있다.
- 결과는 언제나 그렇듯 당신의 서비스 트랜잭션에 맞게….
